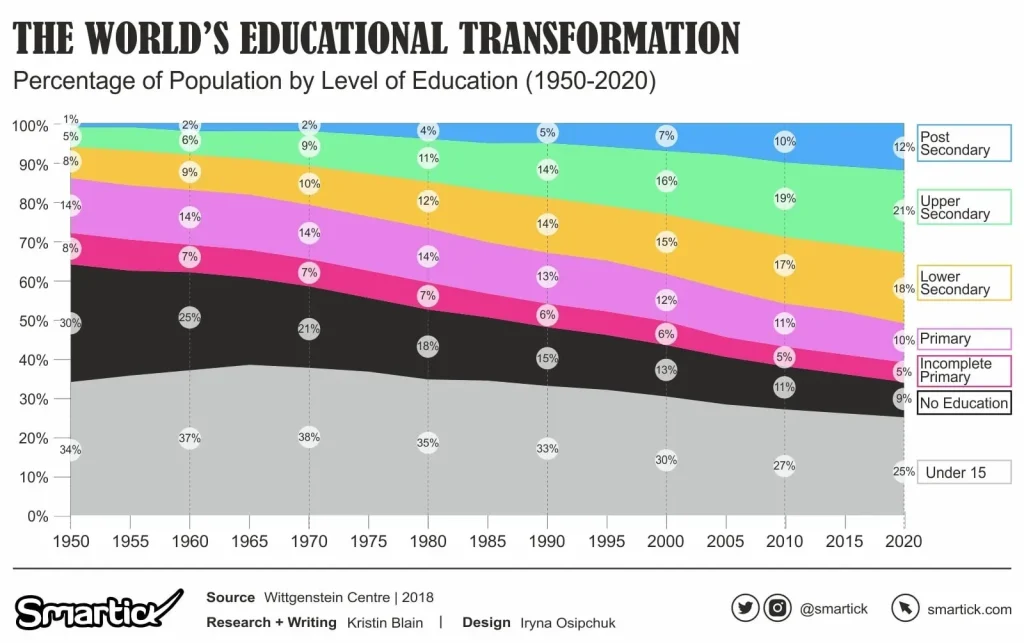
World Education Shifts are reshaping how we think about access, equity, and participation in classrooms around the globe. As digital tools broaden opportunities, education access is expanding in some regions while remaining stubbornly uneven in others. Educators, policymakers, families, and students navigate a landscape of evolving curricula and a renewed emphasis on equity through inclusive education strategies. This article examines how access, equity, and new learning models intersect to redefine learning in the 21st century, offering education policy insights. It also highlights practical strategies for schools, communities, and governments to translate these shifts into better learning outcomes for all students.
Beyond the headline, global schooling reform points to a broader shift toward more adaptable learning ecosystems that blend digital and face-to-face experiences. This transformation is described with terms such as inclusive education reform, equitable access to schooling, and competency-based progression. Educators and policymakers are testing blended instruction, microcredentials, and modular curricula that reflect real-world skills while expanding participation. Effective policy and cross-sector partnerships help translate these ideas into scalable improvements for learners across diverse contexts.
World Education Shifts: A Framework for Access and Equity
World Education Shifts frame how access to education intersects with opportunity and participation. In this framework, education access becomes the entry point for social mobility, and education equity guides how opportunities are distributed across diverse communities.
To operationalize this framework, policymakers and schools must align with new learning models and inclusive education strategies, ensuring that digital tools augment rather than widen gaps. Education policy insights emphasize governance, funding, and accountability to sustain progress toward equitable outcomes.
Expanding Education Access: From Urban Hubs to Rural Pathways
Access trends show urban centers benefiting from robust digital infrastructure, while rural communities continue to face unreliable internet and device shortages. Expanding education access requires offline-first content, low-bandwidth delivery, and community-based learning hubs that bring resources closer to learners.
Partnerships with libraries, non-profits, businesses, and local governments—along with family engagement—help place devices on loan and subsidize data. When strategies are grounded in local needs and multilingual resources, education equity starts translating into real learning outcomes across regions.
Inclusive Education Strategies that Elevate Equity
Inclusive education strategies shift from a one-size-fits-all approach to tailoring learning experiences through universal design for learning (UDL) and culturally responsive pedagogy. These approaches help diverse learners access content and demonstrate understanding in multiple ways.
Equity-oriented investments—such as targeted tutoring, assistive technologies, safe transportation, and scholarships for marginalized students—turn policy into practice and ensure every learner can participate meaningfully in the classroom and beyond.
New Learning Models and the Path to Mastery
Blended learning, project-based learning, and competency-based education blend traditional instruction with digital resources to enable personalized pacing, authentic tasks, and flexible progression. Microcredentials and modular curricula align learning with labor market needs and clearly signal demonstrated skills.
Implementing these models requires professional development for teachers, data-driven instruction, and robust learning analytics that identify at-risk students and support targeted interventions, helping learners move toward mastery rather than seat time.
Policy Insights that Sustain Education Progress
Education policy insights emphasize sustained investment in core learning resources, transparent data on access and outcomes, and governance models that empower local actors while maintaining national standards.
Policies should encourage flexible delivery models, inclusive assessment practices, and cross-sector collaboration among education, health, housing, and social services to address social determinants that influence learning success.
Collaboration and Community Support: Building Local Learning Ecosystems
No single solution will realize World Education Shifts; collaboration among schools, families, communities, and the private sector is essential to expanding education access and advancing education equity.
Community learning centers, after-school programs, and transparent parental engagement extend learning beyond the classroom, while local partnerships help ensure new learning models translate into meaningful outcomes for all students.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do World Education Shifts address education access across regions, and what strategies expand access?
World Education Shifts expand education access by combining offline-enabled content, low-bandwidth delivery, and device loan programs with community-based learning hubs. In urban areas with strong connectivity, online courses and flexible schedules broaden participation, while in rural or underserved regions strategies like smartphone-based learning, radio broadcasts, and partnerships help bridge gaps. The goal is practical, scalable access that removes barriers to enrollment and persistence.
Why is education equity central to World Education Shifts, and how do inclusive education strategies support this goal?
Education equity means tailoring learning to diverse needs so every student can reach their potential. Inclusive education strategies—Universal Design for Learning (UDL), multilingual resources, disability accommodations, and culturally responsive pedagogy—embed equity across curricula, assessments, and school culture. Targeted funding, safe transportation, and scholarships reinforce these efforts and help make equity a durable outcome.
What are the main components of new learning models in World Education Shifts, and how do they affect learner outcomes?
New learning models in World Education Shifts blend in-person instruction with digital resources, enabling personalized pacing and richer feedback. Core components include blended learning, asynchronous modules, project-based learning, and competency-based education, shifting focus from seat time to demonstrated mastery. Microcredentials and industry partnerships provide job-relevant skills, supported by data-driven teacher development.
What education policy insights guide World Education Shifts toward sustainable improvements?
Education policy insights guide sustainable change through sustained investment, transparent data on access and outcomes, and governance models that empower local actors while maintaining national standards. Policies should align funding with equity goals, support flexible delivery and inclusive assessment practices, and foster cross-sector collaboration to address social determinants influencing learning success.
How can technology function as an enabler in World Education Shifts without widening gaps?
Technology should enable, not replace, good pedagogy. In World Education Shifts, learning analytics, AI-driven tutoring, and digital tools support personalized learning while safety, accessibility, and affordability are prioritized. Ensuring universal device access, accessible content, and digital literacy helps close the equity gap rather than widen it.
What practical steps can schools and communities take to implement World Education Shifts with inclusive education strategies for all learners?
Practical steps include establishing community learning centers, offering after-school programs, and engaging families with transparent communication. Use locally relevant materials, multilingual resources, and safe transportation to improve participation. Strengthen partnerships with NGOs and businesses and continuously monitor progress to ensure inclusive education strategies reach every learner.
| Section | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Access Trends in a Bilateral World | Access is expanding in some regions but remains uneven; new learning ecosystems emerge through mobile platforms, libraries, and partner institutions; urban areas with strong digital infrastructure see online/hybrid expansion, while rural/underserved areas face unreliable internet, device shortages, and transportation barriers; solutions emphasize offline-enabled content, low-bandwidth delivery, locally relevant materials, multilingual resources, flexible enrollment, and partnerships to extend access. |
| Equity as a Driving Principle in Education | Equity means tailoring learning experiences to diverse needs and ensuring opportunities for all to reach their potential. World Education Shifts advocate inclusive strategies addressing linguistic diversity, disability, gender norms, and migration status; Universal Design for Learning (UDL) plus targeted supports (assistive tech, tutoring, culturally responsive pedagogy) make equity actionable within curriculum, classroom practices, assessments, and school culture; additional funding, safe transportation, and scholarships support high-need groups. |
| New Learning Models Driving Change | Blended learning blends in-person instruction with digital resources for personalized pacing and feedback; asynchronous modules support flexible schedules; project-based learning and competency-based education emphasize mastery over seat time; microcredentials and modular curricula align with labor-market needs; partnerships with industry certify competencies; teachers require professional development in data-driven instruction and digital pedagogy. |
| Technology as an Enabler, Not a Solution | Technology enhances learning but is not a silver bullet; effective use combines tech with human-centered pedagogy; learning analytics reveal engagement patterns and target interventions; AI supports tutoring and feedback while automating routine tasks; equitable access, affordability, and inclusivity are essential to prevent widening gaps; technology should extend pedagogy, supported by teacher development and community support. |
| Policy Insights to Accelerate Positive Change | Sustained investment in core resources, transparent data on access and outcomes, and governance that empowers local actors while upholding national standards are key; policies should fund flexible delivery models, inclusive assessments, and strong teacher pipelines; cross-sector collaboration (education, health, housing, social services) addresses social determinants and supports experimentation with new approaches. |
| The Role of Collaboration and Community Support | Collaboration among schools, families, communities, and the private sector is essential; community learning centers, after-school programs, libraries, and workforce training extend learning beyond classrooms; parental engagement and transparent progress communication build trust; localized, culturally relevant resources and neighborhood mentoring help make equity a lived reality. |
| Case Studies and Real-World Implications | Urban blended-learning pilots show improved engagement and mastery in math and science; offline-first content and solar-powered devices support learning in areas with limited connectivity; competency-based pathways and microcredentials align curricula with evolving job markets and demonstrate skills over time; learner-centered approaches yield clearer pathways from education to employment. |
Summary
World Education Shifts describe a global movement toward broader access, deeper equity, and innovative learning models that together redefine what it means to learn in the 21st century. This evolution requires context-aware, affordable solutions that remove practical and cultural barriers while embracing digital tools thoughtfully. By combining inclusive pedagogy, universal design, and targeted supports with responsible technology use, education systems can improve outcomes for all learners. Sustained policy investment, cross-sector collaboration, and active community engagement are essential to turn these shifts into durable improvements in learning experiences and life opportunities. The path forward centers on the learner, ensuring that no student is left behind as access expands and new models connect learning to meaningful work.