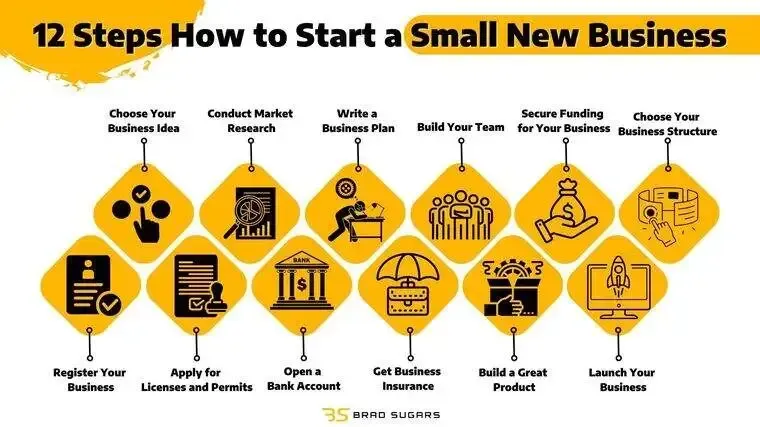
Start a Successful Small Business is a bold aspiration that blends ambition with practical planning. This guide translates a big idea into a step-by-step business plan you can apply from launch to growth, making the journey feel achievable. From validating demand to shaping your value proposition, you’ll find practical actions, templates, and checklists designed for real people. You’ll learn how to run quick market tests, interpret customer signals, and iterate with discipline so your early efforts translate into momentum. Whether you’re launching solo or with a partner, the framework helps you manage risk, stay focused, and turn a spark of potential into sustainable results.
Beyond the surface of the idea, the journey involves launching a profitable venture, establishing a lean startup, and validating your market with real customers. For entrepreneurship for beginners, think in terms of a structured pathway: a clear mission, a tested value promise, and a practical roadmap that translates ideas into revenue. The emphasis shifts from perfect products to iterative learning, guided by business planning tips and a disciplined go-to-market approach. By reframing the topic with terms like venture creation, market fit, and scalable operations, you signal to readers and search engines that the concepts are broad, interconnected, and actionable.
Start a Successful Small Business: From Validation to Growth
Starting a successful small business begins with disciplined validation. Treat your idea as a testable hypothesis, define the problem you’re solving, and identify the specific group of people who experience it. Estimate the total addressable market (TAM) and assess the serviceable obtainable market (SOM) within your price range and geography. These numbers don’t have to be exact; they provide a compass for prioritization and a framework for the next decisions.
Practical validation comes from customer interviews, surveys, and a simple landing page that captures interest or pre-orders. Use the small business startup steps to guide this phase: articulate a clear value proposition, test pricing models, and observe willingness-to-pay signals. Keep the prototype lean; a minimum viable concept that demonstrates core value is enough. As you gather feedback, refine the value proposition (your unique selling proposition) so it resonates with your target audience. If signals are weak, pivot or pause; if signals are strong, you can move forward with confidence.
Idea Validation and Market Reality for Sustainable Growth
Once you have a testable concept, anchor your next moves in concrete market reality. Clarify the problem, confirm you’re solving a real pain, and define your ideal customer profile (ICP) and the outcomes you promise. This approach echoes the small business startup steps you already took and helps you avoid chasing vanity metrics.
To keep momentum, translate insights into a lean, actionable plan: outline pricing, channels, and a minimal viable offering. Use a step-by-step business plan to stay aligned across the team and to guard against scope creep. If early signals are weak, adjust quickly; if they’re strong, lock in assumptions and prepare for a more ambitious launch. These business planning tips help you stay disciplined during rapid learning.
Niche, Audience, and Product-Market Fit: Sharpening Focus
Clarity about your niche matters more than chasing broad reach. Define your ideal customer profile: who they are, what job they’re trying to get done, what alternatives they currently rely on, and what outcomes matter most to them. Answering these questions helps you tailor a single, compelling message that resonates across all marketing channels. You’ll want to answer questions like where these customers spend time and what language they respond to, and map three to five personas and their buyer journeys.
Narrow focus early is a proven path to faster growth. It enables you to create a sharper product or service, a targeted pricing structure, and a coherent brand story. It also makes it easier to test different channels and iteratively improve. As you define your audience, outline three to five personas and map their buyer journeys to inform your marketing plan and content strategy, a cornerstone of entrepreneurship for beginners.
From Idea to Plan: A Step-by-Step Blueprint
A clear path from concept to operation begins with a step-by-step blueprint that covers people, process, and capital. Here is a practical blueprint you can adapt: 1) Clarify value and confirm demand. 2) Define your business model and pricing. 3) Build a minimal viable offering. 4) Validate operations and logistics. 5) Create a lean marketing and sales plan. 6) Draft a concise business plan for growth. 7) Build a financial foundation. 8) Establish legal structure and governance. 9) Launch and learn.
This framework acts as a step-by-step business plan you can adapt, with a lean budget and quick feedback loops. Each step should be validated with customer feedback and kept simple to conserve cash. By documenting assumptions and learning in real time, you maintain agility while moving toward product-market fit.
Strategic Growth and Ongoing Optimization
Once you’ve launched, the focus shifts from validation to growth while maintaining discipline around costs and quality. Growth is rarely linear, so cultivate a culture of learning and experimentation. Regularly revisit your niche and customer insights to ensure you’re solving the most important problems for your audience. Invest in a scalable marketing framework, a repeatable sales process, and an operations backbone that can handle rising demand without sacrificing customer experience.
In the context of entrepreneurship for beginners, curiosity, resilience, and the willingness to adapt are invaluable. By leaning on a structured, test-and-learn approach and the core discipline of testing, learning, and iterating, you’ll increase your odds of building a durable enterprise rather than a one-off. The payoff—independence, impact, and the chance to turn your passion into a scalable venture—comes with patience and sustained execution.
Marketing, Branding, and Online Presence for Credibility and Reach
A credible brand and a strong online presence are non-negotiable for today’s small businesses. Start by choosing a name that reflects your value and reserve a matching domain. Then craft a simple website that clearly communicates your mission, target audience, and the problems you solve. Content that educates, entertains, and demonstrates your expertise will attract organic traffic and establish trust. Social media should amplify your message, not distract from it; select a few channels where your audience is most active and publish consistently.
Your marketing plan should align with the customer journey you defined earlier. Create content that helps your audience research options, compare offerings, and decide. Use case studies, testimonials, and data-backed results to reinforce credibility. A well-executed online strategy can significantly reduce customer acquisition costs and accelerate momentum in the early stages of your business. Track metrics like CAC, LTV, retention, and activation to ensure marketing investments translate into sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the first step to Start a Successful Small Business and validate your idea?
Treat your idea as a testable hypothesis: define the problem you’re solving, identify your target customers, and estimate the market size (TAM) and obtainable segment (SOM). Validate quickly with customer interviews, surveys, and a simple landing page to gauge interest and willingness to pay. Follow the small business startup steps and develop a lean value proposition before building a prototype; if signals are weak, pivot or pause, and if strong, move toward a formal plan.
How can you use a step-by-step business plan for entrepreneurship for beginners?
A step-by-step business plan guides you from concept to operation. Start with clarifying the value you offer, then define your business model and pricing, build a minimal viable offering, and validate operations and logistics. Next, craft a lean marketing and sales approach, draft a concise growth plan, and establish basic finances and governance. For Start a Successful Small Business, this framework keeps beginners focused and outcomes-oriented.
Why is niche, audience, and product-market fit critical when Start a Successful Small Business?
Clarity on your niche and audience enables a single, compelling message that resonates across channels. Outline three to five buyer personas and map their journeys to inform your marketing plan, pricing, and product decisions. Narrow focus early to accelerate product-market fit and growth for Start a Successful Small Business.
What are essential business planning tips for marketing, branding, and online presence?
Start with a credible brand and online presence: choose a name, reserve a domain, and craft a simple website that explains your mission and the problems you solve. Build content that educates and demonstrates your expertise, and select a few social channels aligned with your audience. Your plan should align with the customer journey, leverage case studies and testimonials, and track metrics like CAC, LTV, and churn to optimize results—these are core business planning tips.
How should you measure progress and iterate toward scale in entrepreneurship for beginners?
Track key performance indicators such as revenue growth, gross margin, customer acquisition cost, activation, retention, and lifetime value. When a metric deviates, investigate the root cause, adjust your approach, and measure again. An analytics mindset helps beginners learn what drives value and when to reallocate resources for growth.
What does growth and ongoing optimization look like after launch for Start a Successful Small Business?
Growth requires discipline: regularly revisit your niche and customer insights to stay relevant, and invest in a scalable marketing framework, a repeatable sales process, and an operations backbone. Maintain lean experimentation, monitor core metrics, and iterate on product, pricing, and processes so you can scale thoughtfully and sustainably.
| Section | Key Points | Actions / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Idea validation & market reality | Treat idea as a hypothesis; define the problem and target users; estimate TAM and SOM; rely on data to prioritize. | Interview customers, run surveys, and use a simple landing page; test value proposition, pricing, and willingness-to-pay; aim for a minimum viable concept; pivot if signals are weak. |
| Niche, audience, and product-market fit | Clarify niche; define ideal customer profile; tailor messaging; map buyer journeys; focus to accelerate growth. | Outline 3–5 personas; identify where customers spend time; craft a single resonant message; align marketing, sales, and content with the buyer journeys. |
| From idea to plan: 9-step blueprint | Provide a practical, end-to-end plan covering people, process, and capital. | Steps 1–9: 1) Clarify value & demand; 2) Define business model & pricing; 3) Build minimal viable offering; 4) Validate operations; 5) Lean marketing & sales plan; 6) Draft growth plan; 7) Build financials; 8) Establish legal structure; 9) Launch & learn. |
| Strategic growth & ongoing optimization | Shift from validation to growth with cost discipline; cultivate learning; revisit niche; scalable framework. | Foster culture of experimentation; optimize based on data; invest in analytics; align with customer insights. |
| Marketing, branding & online presence | Build credible brand and accessible online presence; domain, simple website, content that educates; select key channels. | Name and domain; publish content; case studies; testimonials; focus on few channels aligned with customer journey. |
| Measuring progress & iterating toward scale | Track KPIs to guide decisions; revenue growth, margins, CAC, activation, retention, LTV; data-driven adjustments. | Monitor metrics; investigate deviations; implement targeted adjustments; reallocate resources for impact. |
Summary
Start a Successful Small Business is a journey of disciplined exploration and continuous refinement. This descriptive path surveys how to move from initial validation to a scalable operation by focusing on niche clarity, lean product development, cash discipline, and relentless testing. By following a practical, step-by-step plan and continually measuring progress, aspiring entrepreneurs can turn a simple idea into a durable enterprise. The framework emphasizes curiosity, resilience, and thoughtful growth, helping you build independence, impact, and long-term success. Start a Successful Small Business isn’t just about launching a venture—it’s about crafting a sustainable, evolving enterprise that can adapt to changing markets and customer needs.