Risk Management for Businesses is essential in today’s volatile economy, helping leaders anticipate disruptions and protect value by prioritizing critical processes, assets, and stakeholders. It addresses threats from economic shocks, supply chain volatility, and changing consumer demand so you can act before a crisis, preserving cash flow and reputation. A solid approach combines governance, enterprise risk management, and disciplined risk reporting with business continuity planning to keep operations steady, enabling rapid recovery, informed investment choices, and accountable leadership across functions. By integrating risk insights into strategy and capital allocation, organizations improve financial risk mitigation and align operational risk management with core objectives, while training teams to recognize early warning signals and respond decisively. This descriptive overview outlines practical steps to embed risk management across people, processes, and technology, strengthening resilience from day one by leveraging data, scenario analysis, and continuous learning.
Beyond formal frameworks, organizations can view risk as a holistic governance challenge that spans people, processes, and technology, emphasizing risk governance, risk oversight, and a culture of openness. This perspective integrates strategy with resilience planning, scenario analysis, and continuous monitoring to identify threats before they become crises. Aligned with corporate risk management principles, it helps leaders balance exposure, capital allocation, and performance under uncertainty. A data-informed mindset and cross-functional collaboration translate risk signals into timely decisions that support business continuity planning and steady operations. The aim is a resilient enterprise that detects threats early, allocates resources wisely, and preserves value through volatility.
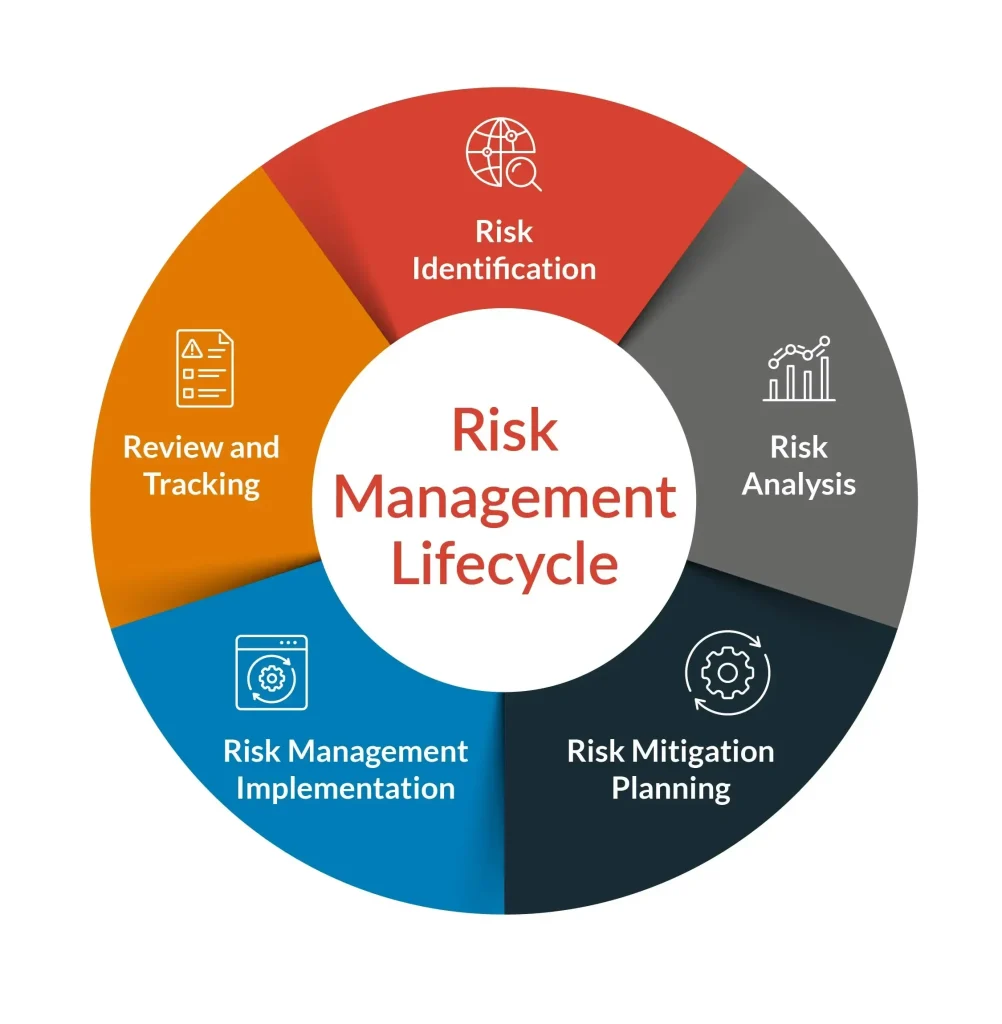
Risk Management for Businesses: Building a Robust Enterprise Risk Management Framework
In today’s volatile economy, risk management hinges on a structured approach that covers financial, operational, strategic, and compliance risks. Enterprise risk management (ERM) provides a centralized, organization-wide process to identify risks, quantify their likelihood and impact, and align mitigation with the company’s strategic objectives. By tying risk appetite to strategy, ERM helps leadership see the full exposure to economic shocks and makes risk-informed decisions a routine part of planning.
A robust ERM framework rests on clear risk governance, explicit risk appetite, and disciplined identification and assessment. It also enshrines controls and mitigations, plus ongoing monitoring and reporting. When risk information flows to leadership in dashboards and metrics, teams can act quickly to reduce exposure, capitalize on opportunities, and sustain performance through volatility.
Diversifying Revenue Streams to Withstand Economic Shocks and Protect Cash Flows
Relying on a single product, customer segment, or geography concentrates risk and makes a downturn harder to absorb. Diversification—across products, channels, and markets—smooths cash flow, expands the demand base, and strengthens resilience during economic shocks. A diversified portfolio also supports more stable margins by spreading exposure across multiple revenue sources.
Practical diversification steps include exploring adjacent market opportunities, developing scalable offerings, and building multi-channel distribution. By embedding scenario analysis into growth plans and aligning pricing, capacity, and marketing with recovery timelines, businesses can reduce vulnerability and improve financial flexibility when demand shifts or supply constraints arise.
Strengthening Liquidity, Working Capital, and Financial Risk Mitigation
Liquidity is the lifeblood of a business during downturns. Strong working capital management—supported by cash flow forecasting, access to credit facilities, and prudent liquidity buffers—helps a firm weather economic shocks and maintain operations. Financial risk mitigation actions, including prudent hedging and diversified financing, reduce the impact of volatility on margins and cash generation.
Implementing disciplined liquidity governance means forecasting best, worst, and most likely scenarios, establishing lines of credit before they’re needed, and renegotiating terms with suppliers and customers to optimize cash conversion. Maintaining a liquidity reserve and monitoring key liquidity indicators provides resilience, while a proactive approach to receivables, payables, and inventory prevents cash crunches from derailing strategic initiatives.
Business Continuity Planning and Operational Risk Management: A Practical Integration
Business continuity planning (BCP) is the proactive counterpart to day-to-day operations, ensuring critical processes keep running during disruptions. Integrated with operational risk management, BCP addresses process failures, IT outages, and supply chain shocks by defining recovery objectives, ownership, and escalation paths. This integration reduces downtime and preserves customer value even when external conditions change.
Operational risk management focuses on the routines that keep the business functioning, such as supplier reliability, cyber security, and regulatory compliance. Practical steps include documenting end-to-end processes, enabling cross-training, and maintaining tested disaster recovery plans and incident response playbooks. Regular drills and audits turn risk awareness into actionable readiness, supporting faster recovery when shocks occur.
Scenario Planning, Contingency Budgeting, and Data-Driven Decision-Making
Scenario planning translates uncertainty into concrete action by developing base, best, and worst-case futures with explicit triggers for strategic shifts. Contingency budgeting allocates resources differently under each scenario, detailing where to reallocate capital, adjust pricing, or scale capacity. Rolling forecasts keep leadership informed as conditions evolve, enabling timely pivots to sustain performance.
Data-driven decision-making turns uncertain data into actionable insights. Investing in analytics improves forecasting accuracy, risk detection, and the simulation of what-if scenarios. AI-enabled monitoring and automated reporting speed up risk detection, while a strong emphasis on cybersecurity and data protection safeguards information assets during periods of disruption.
Culture, Governance, and Transparent Reporting: Embedding ERM into the Organization
A resilient organization cultivates a risk-aware culture where clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability are embedded in everyday decisions. Governance structures—clear ownership, risk appetite alignment, and board-level reporting—ensure that enterprise risk management becomes part of strategic execution rather than a separate process. This cultural foundation makes risk information actionable and trusted.
Transparent reporting and continuous improvement are essential to sustaining resilience. Regular risk communications, performance incentives aligned with risk priorities, and formal lessons learned from incidents or near-misses feed back into the ERM cycle. By centering governance and culture, companies strengthen business continuity planning, bolster trust with stakeholders, and enhance long-term value in the face of ongoing volatility.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Risk Management for Businesses help organizations navigate economic shocks and protect liquidity?
Risk Management for Businesses uses enterprise risk management (ERM) to identify, quantify, and mitigate risks that come with economic shocks. Through scenario planning, liquidity buffers, diversification, and ongoing risk monitoring, it helps preserve cash flow and sustain operations during volatility.
In Risk Management for Businesses, how does business continuity planning strengthen resilience?
Business continuity planning is a core pillar of Risk Management for Businesses, ensuring critical operations can continue or quickly recover after disruptions. It aligns with ERM governance, defines recovery objectives, and is tested through drills and incident response activities.
What are practical steps for financial risk mitigation within Risk Management for Businesses?
Financial risk mitigation in Risk Management for Businesses includes cash-flow forecasting, hedging currency or interest-rate exposure, securing insurance coverage, and building contingency funding to stabilize margins and protect the balance sheet.
How does enterprise risk management integrate with operational risk management to cover day-to-day risks?
Risk Management for Businesses coordinates across risk domains by integrating enterprise risk management with operational risk management. This enables mapping of critical processes, identification of single points of failure, and implementation of controls and dashboards to mitigate daily operational risks.
What is the role of risk governance and risk appetite in Risk Management for Businesses?
In Risk Management for Businesses, risk governance defines ownership and reporting lines, while risk appetite sets tolerances for risk-taking. Regular reviews ensure strategic decisions stay within defined limits and inform leadership.
How can scenario planning and contingency budgeting be used in Risk Management for Businesses to prepare for multiple futures?
Scenario planning in Risk Management for Businesses creates base, optimistic, and worst-case plans with explicit triggers for action. Contingency budgeting allocates resources under each scenario, and rolling forecasts keep plans aligned with evolving conditions.
| Area | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | In today’s volatile economy, businesses face uncertainties and disruptions. Risk Management for Businesses is a strategic imperative that guides organizations to weather shocks, build resilience, and sustain performance by applying practical, evidence-based risk strategies. |
| Understanding the Stakes | Economic shocks can cascade through a business: supplier failure, inflation eroding margins, and sudden demand drops. Small and medium-sized enterprises often feel the impact more acutely due to tighter liquidity. The core objective of Risk Management for Businesses is to identify, quantify, and mitigate risks before they derail strategic goals. |
| A Structured Framework for Resilience | Enterprise risk management (ERM) is an organization-wide process that identifies risks, assesses likelihood and impact, and implements controls to reduce exposure. A robust ERM aligns risk appetite with strategy, ensures accountability, and fosters a culture where risk information informs decision-making. Key components include: – Risk governance: clear ownership, approval, and risk reporting to leadership – Risk appetite and tolerance: explicit thresholds guiding investments and planning – Risk identification and assessment: ongoing discovery of financial, operational, strategic, and compliance risks with scenario analysis and stress testing – Controls and mitigations: policies, insurance, hedging, and other measures – Monitoring and reporting: dashboards and metrics that keep risk visibility current |
| Strategies to Weather Economic Shocks | The most effective risk management is proactive, not reactive. The following strategies are practical and directly tied to Risk Management for Businesses. |
| 1) Diversify Revenue Streams | Diversification reduces concentration risk across product lines, channels, or regions. Practical steps include: – Explore adjacent markets or new segments – Develop affordable, scalable offerings – Build multi-channel distribution to reduce dependence on a single channel |
| 2) Strengthen Liquidity and Working Capital Management | Liquidity is critical during shocks. Actions: – Forecast cash flow with scenario planning (worst-case and recovery) – Establish credit facilities and maintain lender relationships – Tighten working capital: renegotiate terms, optimize inventory, accelerate receivables – Build a liquidity reserve (cash or lines of credit) |
| 3) Optimize Costs with a Strategic Lens | Strategic cost control protects margins while preserving core capabilities. Steps: – Identify non-essential expenditures and plan staged reductions – Invest in automation and process improvements for sustainable savings – Prioritize high-impact, revenue-enabling activities; pause low-value initiatives during stress |
| 4) Scenario Planning and Contingency Budgeting | Translate uncertainty into action via scenarios and contingency budgeting: – Develop base, best, worst scenarios with triggers – Create contingency budgets and resource reallocation plans – Use rolling forecasts to keep plans current |
| 5) Supply Chain Diversification and Supplier Risk Management | Mitigate supply chain shocks by: – Mapping critical suppliers and assessing risk profiles – Building redundancy and safety stocks – Collaborating on risk-reduction initiatives with suppliers |
| 6) Insurance, Hedging, and Financial Instruments | Transfer or offset risk where possible through: – Reviewing gaps in insurance (property, business interruption, cyber, etc.) – Using hedging for currency, interest rate, or commodity volatility – Aligning hedging/insurance with risk appetite |
| 7) Data-Driven Decision-Making and Technology Adoption | Leverage data to improve forecasting and risk detection: – Invest in analytics and scenario simulations – Implement automation/AI for monitoring – Strengthen cybersecurity and data protection |
| 8) Culture, People, and Governance | A risk-aware culture supports governance and strategy: – Training, clear roles, and risk communications – Integrate risk into planning, performance reviews, and incentives – Establish crisis governance and incident response playbooks |
| Operational Risk Management in Practice | Focuses on day-to-day processes and systems: – Document critical processes and identify single points of failure – Cross-train employees – Maintain IT disaster recovery and data backups with tested procedures – Conduct regular compliance audits – Develop incident response drills |
| The Role of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) | ERM provides the big-picture view and aligns risk with strategic objectives: – Formal risk registry with owners, controls, and residual risk – Regular risk appetite reviews – Transparent risk reporting to leadership and board – Continuous improvement from incidents or near-misses |
| Case Examples and Real-World Insights | Real-world examples show diversified supplier bases, contingency inventories, rolling forecasts, and scenario planning enabling smoother cash flow, fewer disruptions, and faster recovery when shocks occur. |
| Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement | Track KRIs and adjust strategy using metrics such as: – Reduction in cash burn and improved liquidity coverage – Fewer disruptions and faster recovery – Margin resilience through pricing, terms, and cost control – Stronger balance sheet metrics (debt/equity, interest coverage) – Regular risk reporting that informs strategy |
Summary
Conclusion