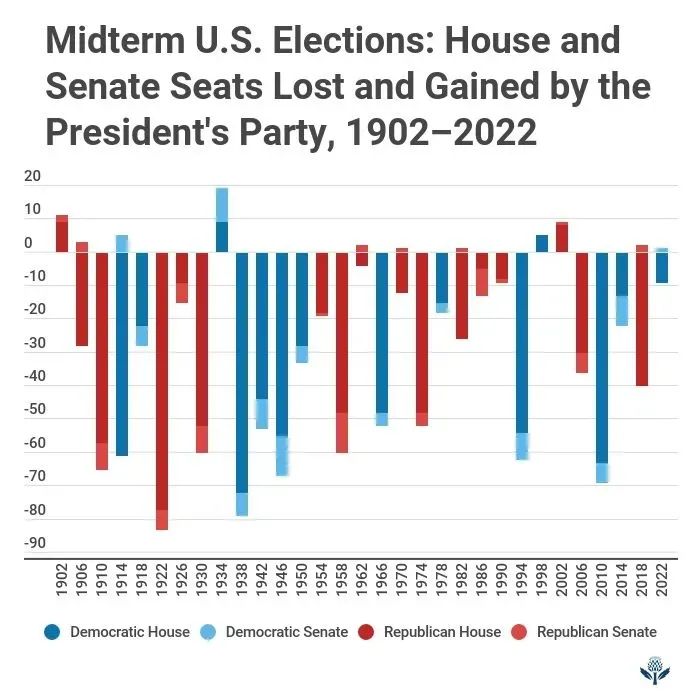
Elections Demystified opens as a clear, practical guide to how voting works for everyday readers. This concise primer explains how elections work, from registration to ballot counting, in plain language. From primaries through the general election and the role of polls, it links big concepts to step-by-step actions voters can take, using plain language, practical analogies, and real-world examples. You’ll pick up essential phrases like voting basics and practical steps, making the voting process less intimidating. Whether you vote this year or simply want to understand the system, this guide invites you to participate with confidence, curiosity, and a clearer sense of your voice in public life.
Think of the political process as a citizen’s roadmap to choosing leaders and shaping policy. The overview reframes the journey from ballots and ballots-related decisions to the mechanics of participation, emphasizing registration checks, casting ballots, tallies, and official outcomes. It connects concepts such as political engagement, civic literacy, and decision-making cycles, using related terms like election dynamics, campaign timelines, and public opinion gauges to build a web of meaning that supports informed involvement.
1) The Big Picture: How Elections Work (Elections Demystified)
Elections are a structured cycle that lets citizens influence who represents them and which policies take priority. When you ask how elections work, the answer is a sequence of practical steps: voter registration to establish who can vote, the casting of ballots, the counting of those ballots, and the certification that finalizes results. These elements—the core components of the election fundamentals—form the backbone of how elections work in democracies around the world.
Across countries and jurisdictions, the big picture follows a familiar flow: primaries or caucuses to select nominees, then a general election where voters choose among those nominees. As Elections Demystified explains, this cycle aims to be fair, transparent, and accessible so eligible voters can participate with confidence. Understanding these pieces helps readers navigate headlines and policy debates with clarity and skepticism where needed, reinforcing the idea of election fundamentals.
2) Primary Elections Explained: From Nominees to Party Strategy
Primary elections explained show how parties decide which candidate will appear on the general election ballot. Formats vary widely: closed primaries require party registration to participate, open primaries let any registered voter choose a party’s ballot, and caucuses or semi-open models can reorder the process entirely. By exploring these variants, you can see why turnout, information about candidates, and strategic voting matter in this phase.
This phase narrows the field to a party’s official nominee and often shifts campaign emphasis based on delegate rules or direct nomination. The way primaries unfold also helps explain why polls during the primary season can move quickly and why some races look settled early while others stay competitive into spring. Grasping this helps readers anticipate general election dynamics and the path toward the general ballot, reinforcing how elections work in practice.
3) Reading Polls and Understanding General Election Polls
Polls are probabilistic snapshots of public opinion at a moment in time, and general election polls provide a sense of momentum after candidates emerge from primaries. They can reveal where support is strongest, how issues resonate, and where turnout could matter.
To read polls well, examine the sample size, margin of error, conduct date, and whether the poll targets likely voters or registered voters. Polls are informative tools within the broader information landscape of how elections work; they do not decide outcomes on their own and must be interpreted alongside debates, policy positions, and candidate records.
4) Voting Basics and the Voting Process for Beginners
The voting process for beginners typically starts with verifying eligibility and registration status well before Election Day. Then you locate your polling place, learn voting hours, and consider alternatives like early voting or mail-in ballots if available.
Beyond casting a vote, the voting basics include reviewing the ballot, understanding candidates and ballot measures, and bringing any required identification. Many jurisdictions offer sample ballots or nonpartisan guides to help you compare options and cast an informed vote, making the voting process approachable for new participants.
5) Participation and Information Literacy: Understanding Political Participation
Understanding political participation means looking beyond the ballot to how people engage with information, communities, and public issues. This broader view helps you see how participation shapes policy and accountability, not just the moment of voting.
Practical steps to improve participation include following multiple reputable sources, checking the dates and context of polls and claims, learning local registration rules, and engaging in respectful dialogue with others who hold different viewpoints. Building this literacy supports well-informed civic engagement and responsible participation.
6) Election Fundamentals: From Registration to Certification and Civic Confidence
Election fundamentals describe the essential lifecycle of an election: ensure you are registered, confirm eligibility, study the ballot, and understand how votes are counted and certified. This framework helps demystify the process and connects the day-to-day actions of voters to the broader goal of fair representation.
To participate with confidence, diversify information sources, read poll context, verify dates, and learn local voting rules so your participation reflects both your choices and the civic process. Keeping these fundamentals in mind supports transparent elections and informed, civically engaged participation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Elections Demystified: How do elections work?
Elections Demystified explains the core cycle—registration, casting ballots, vote counting, and certification—while noting that mechanics vary by country or region. The typical flow includes primaries to select nominees and a general election to choose among them, all designed to be fair, transparent, and accessible.
Elections Demystified: What does primary elections explained mean, and why do they matter?
Primary elections explained show how parties narrow the field to a single nominee. Formats vary (closed, open, semi-open, caucuses), and delegates may be involved in some systems. This phase shapes the general election by signaling party directions and influencing campaign strategies.
Elections Demystified: How should I read general election polls?
General election polls provide a snapshot of public opinion, with factors like sample size, margin of error, and whether it measures likely or registered voters. They inform discussion but do not determine outcomes, so read polls critically alongside other signals and events.
Elections Demystified: What is the voting process for beginners?
For beginners, start by verifying eligibility and registration, then locate your polling place and voting hours. Review the ballot in advance, bring any required ID, cast your ballot, and use any available confirmation to verify your vote was counted. Many areas offer early voting or mail-in options as well.
Elections Demystified: What are voting basics and how can I participate?
Voting basics include understanding ballots, local races, and how seats are allocated. Use nonpartisan voter guides, assess candidates’ qualifications, and follow credible sources to participate confidently and stay informed about the political process.
Elections Demystified: How can I improve my understanding of election fundamentals and understanding political participation?
To strengthen your grasp of election fundamentals, practice information literacy: follow multiple reputable outlets, check poll dates and methodologies, learn local voting rules, and engage respectfully with others. This approach helps you participate more meaningfully in the democratic process.
| Topic | Key Points | Practical Takeaways |
|---|---|---|
| The Big Picture: How Elections Work | Elections are a structured cycle with core elements: voter registration, casting ballots, counting, and certification. Mechanics vary by country/region, but the underlying principles—eligibility, ballots, counting, and verification—remain consistent. | Track the cycle to interpret results and commentary more clearly; focus on eligibility, ballots, counting, and verification. |
| Election Structure: Primaries to General | Most elections involve primaries or caucuses to select party nominees, followed by a general election. Some systems use simple majorities, others use proportional representation, which changes how votes translate into representation. | Understand where your vote fits in the process and how different systems affect outcomes. |
| The Primary Process | Formats include Closed, Open, Semi-Open/Semi-Closed, and Caucuses. Primaries may involve delegates or direct nomination; winners often advance to the general election, influencing party direction and campaign viability. | Know your jurisdiction’s rules and how your participation can influence who appears on the ballot and the party’s stance. |
| Reading Polls | Polls are probabilistic snapshots that depend on sampling, question wording, mode, and how “likely voters” are defined. Margins of error indicate precision and turnout assumptions may vary. | Read beyond headlines; check sample size, margin of error, date, and whether the poll targets likely or registered voters. |
| Voting Basics | Steps include verifying eligibility, finding polling places and hours, reviewing the ballot, bringing required ID, casting the ballot, and confirming receipt if available. Knowledge of ballot measures and local races is also important. | Prepare ahead of Election Day; know local rules, options (early voting/absentee), and what you need to bring. |
| Participation and Information Literacy | Informed participation goes beyond voting: engage with credible information, compare sources, and check dates and methodologies for polls and claims. | Follow multiple reputable sources, verify data context and methodology, learn local registration/voting rules, and engage respectfully. |
Summary
Conclusion: Elections Demystified unpacks how voters move from registration to casting ballots, through counting and certification, across diverse systems. Elections Demystified emphasizes that understanding these stages helps voters participate with confidence, critically assess polling data and media coverage, and engage civically with clarity. By grasping the flow from primaries to general elections, interpreting polls, and navigating the voting process, readers can approach politics with information, civility, and greater civic impact.